Stephen Hawking was a scientist known for his work with black holes and relativity, and the author of popular science books like ‘A Brief History of Time.’
Who Was Stephen Hawking?
Stephen Hawking was a British scientist, professor and author who performed groundbreaking work in physics and cosmology, and whose books helped to make science accessible to everyone.
At age 21, while studying cosmology at the University of Cambridge, he was diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Part of his life story was depicted in the 2014 film The Theory of Everything.
Early Life
Hawking was born on January 8, 1942, in Oxford, England. His birthday was also the 300th anniversary of the death of Galileo — long a source of pride for the noted physicist.
The eldest of Frank and Isobel Hawking’s four children, Hawking was born into a family of thinkers.
His Scottish mother earned her way into Oxford University in the 1930s — a time when few women were able to go to college. His father, another Oxford graduate, was a respected medical researcher with a specialty in tropical diseases.
Hawking’s birth came at an inopportune time for his parents, who didn’t have much money. The political climate was also tense, as England was dealing with World War II and the onslaught of German bombs in London, where the couple was living as Frank Hawking undertook research in medicine.
In an effort to seek a safer place, Isobel returned to Oxford to have the couple’s first child. The Hawkings would go on to have two other children, Mary and Philippa. And their second son, Edward, was adopted in 1956.
The Hawkings, as one close family friend described them, were an “eccentric” bunch. Dinner was often eaten in silence, each of the Hawkings intently reading a book. The family car was an old London taxi, and their home in St. Albans was a three-story fixer-upper that never quite got fixed. The Hawkings also housed bees in the basement and produced fireworks in the greenhouse.
In 1950, Hawking’s father took work to manage the Division of Parasitology at the National Institute of Medical Research, and spent the winter months in Africa doing research. He wanted his eldest child to go into medicine, but at an early age, Hawking showed a passion for science and the sky.
That was evident to his mother, who, along with her children, often stretched out in the backyard on summer evenings to stare up at the stars. “Stephen always had a strong sense of wonder,” she remembered. “And I could see that the stars would draw him.”
Hawking was also frequently on the go. With his sister Mary, Hawking, who loved to climb, devised different entry routes into the family home. He loved to dance and also took an interest in rowing, becoming a team coxswain in college.
Education
Early in his academic life, Hawking, while recognized as bright, was not an exceptional student. During his first year at St. Albans School, he was third from the bottom of his class.
But Hawking focused on pursuits outside of school; he loved board games, and he and a few close friends created new games of their own. During his teens, Hawking, along with several friends, constructed a computer out of recycled parts for solving rudimentary mathematical equations.
Hawking entered University College at the University of Oxford at the age of 17. Although he expressed a desire to study mathematics, Oxford didn’t offer a degree in that specialty, so Hawking gravitated toward physics and, more specifically, cosmology.
By his own account, Hawking didn’t put much time into his studies. He would later calculate that he averaged about an hour a day focusing on school. And yet he didn’t really have to do much more than that. In 1962, he graduated with honors in natural science and went on to attend Trinity Hall at the University of Cambridge for a Ph.D. in cosmology.
In 1968, Hawking became a member of the Institute of Astronomy in Cambridge. The next few years were a fruitful time for Hawking and his research. In 1973, he published his first, highly-technical book, The Large Scale Structure of Space-Time, with G.F.R. Ellis.
In 1979, Hawking found himself back at the University of Cambridge, where he was named to one of teaching’s most renowned posts, dating back to 1663: the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics.
Wife and Children
At a New Year’s party in 1963, Hawking met a young languages undergraduate named Jane Wilde. They were married in 1965. The couple gave birth to a son, Robert, in 1967, and a daughter, Lucy, in 1970. A third child, Timothy, arrived in 1979.
In 1990, Hawking left his wife Jane for one of his nurses, Elaine Mason. The two were married in 1995. The marriage put a strain on Hawking’s relationship with his own children, who claimed Elaine closed off their father from them.
In 2003, nurses looking after Hawking reported their suspicions to police that Elaine was physically abusing her husband. Hawking denied the allegations, and the police investigation was called off. In 2006, Hawking and Elaine filed for divorce.
In the following years, the physicist reportedly grew closer to his family. He reconciled with Jane, who had remarried. And he published five science-themed novels for children with his daughter, Lucy.
Stephen Hawking: Books
Over the years, Hawking wrote or co-wrote a total of 15 books. A few of the most noteworthy include:
‘A Brief History of Time’
In 1988 Hawking catapulted to international prominence with the publication of A Brief History of Time. The short, informative book became an account of cosmology for the masses and offered an overview of space and time, the existence of God and the future.
The work was an instant success, spending more than four years atop the London Sunday Times’ best-seller list. Since its publication, it has sold millions of copies worldwide and been translated into more than 40 languages.
‘The Universe in a Nutshell’
A Brief History of Time also wasn’t as easy to understand as some had hoped. So in 2001, Hawking followed up his book with The Universe in a Nutshell, which offered a more illustrated guide to cosmology’s big theories.
‘A Briefer History of Time’
In 2005, Hawking authored the even more accessible A Briefer History of Time, which further simplified the original work’s core concepts and touched upon the newest developments in the field like string theory.
Together these three books, along with Hawking’s own research and papers, articulated the physicist’s personal search for science’s Holy Grail: a single unifying theory that can combine cosmology (the study of the big) with quantum mechanics (the study of the small) to explain how the universe began.
This kind of ambitious thinking allowed Hawking, who claimed he could think in 11 dimensions, to lay out some big possibilities for humankind. He was convinced that time travel is possible, and that humans may indeed colonize other planets in the future.
‘The Grand Design’
In September 2010, Hawking spoke against the idea that God could have created the universe in his book The Grand Design. Hawking previously argued that belief in a creator could be compatible with modern scientific theories.
In this work, however, he concluded that the Big Bang was the inevitable consequence of the laws of physics and nothing more. “Because there is a law such as gravity, the universe can and will create itself from nothing,” Hawking said. “Spontaneous creation is the reason there is something rather than nothing, why the universe exists, why we exist.”
The Grand Design was Hawking’s first major publication in almost a decade. Within his new work, Hawking set out to challenge Isaac Newton’s belief that the universe had to have been designed by God, simply because it could not have been born from chaos. “It is not necessary to invoke God to light the blue touch paper and set the universe going,” Hawking said.
Disease
At the age of 21, Hawking was diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, or Lou Gehrig’s disease). In a very simple sense, the nerves that controlled his muscles were shutting down. At the time, doctors gave him two and a half years to live.
Hawking first began to notice problems with his physical health while he was at Oxford — on occasion he would trip and fall, or slur his speech — but he didn’t look into the problem until 1963, during his first year at Cambridge. For the most part, Hawking had kept these symptoms to himself.
But when his father took notice of the condition, he took Hawking to see a doctor. For the next two weeks, the 21-year-old college student made his home at a medical clinic, where he underwent a series of tests.
“They took a muscle sample from my arm, stuck electrodes into me, and injected some radio-opaque fluid into my spine, and watched it going up and down with X-rays, as they tilted the bed,” he once said. “After all that, they didn’t tell me what I had, except that it was not multiple sclerosis, and that I was an atypical case.”
Eventually, however, doctors did diagnose Hawking with the early stages of ALS. It was devastating news for him and his family, but a few events prevented him from becoming completely despondent.
The first of these came while Hawking was still in the hospital. There, he shared a room with a boy suffering from leukemia. Relative to what his roommate was going through, Hawking later reflected, his situation seemed more tolerable.
Not long after he was released from the hospital, Hawking had a dream that he was going to be executed. He said this dream made him realize that there were still things to do with his life.
In a sense, Hawking’s disease helped turn him into the noted scientist he became. Before the diagnosis, Hawking hadn’t always focused on his studies. “Before my condition was diagnosed, I had been very bored with life,” he said. “There had not seemed to be anything worth doing.”
With the sudden realization that he might not even live long enough to earn his Ph.D., Hawking poured himself into his work and research.
As physical control over his body diminished (he’d be forced to use a wheelchair by 1969), the effects of his disease started to slow down. Over time, however, Hawking’s ever-expanding career was accompanied by an ever-worsening physical state.
How Did Stephen Hawking Talk?
By the mid-1970s, the Hawking family had taken in one of Hawking’s graduate students to help manage his care and work. He could still feed himself and get out of bed, but virtually everything else required assistance.
In addition, his speech had become increasingly slurred, so that only those who knew him well could understand him. In 1985 he lost his voice for good following a tracheotomy. The resulting situation required 24-hour nursing care for the acclaimed physicist.
It also put in peril Hawking’s ability to do his work. The predicament caught the attention of a California computer programmer, who had developed a speaking program that could be directed by head or eye movement. The invention allowed Hawking to select words on a computer screen that were then passed through a speech synthesizer.
At the time of its introduction, Hawking, who still had use of his fingers, selected his words with a handheld clicker. Eventually, with virtually all control of his body gone, Hawking directed the program through a cheek muscle attached to a sensor.
Through the program, and the help of assistants, Hawking continued to write at a prolific rate. His work included numerous scientific papers, of course, but also information for the non-scientific community.
Hawking’s health remained a constant concern—a worry that was heightened in 2009 when he failed to appear at a conference in Arizona because of a chest infection. In April, Hawking, who had already announced he was retiring after 30 years from the post of Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at Cambridge, was rushed to the hospital for being what university officials described as “gravely ill,” though he later made a full recovery.
Research on the Universe and Black Holes
In 1974, Hawking’s research turned him into a celebrity within the scientific world when he showed that black holes aren’t the information vacuums that scientists had thought they were.
In simple terms, Hawking demonstrated that matter, in the form of radiation, can escape the gravitational force of a collapsed star. Another young cosmologist, Roger Penrose, had earlier discovered groundbreaking findings about the fate of stars and the creation of black holes, which tapped into Hawking’s own fascination with how the universe began.
The pair then began working together to expand upon Penrose’s earlier work, setting Hawking on a career course marked by awards, notoriety and distinguished titles that reshaped the way the world thinks about black holes and the universe.
When Hawking’s radiation theory was born, the announcement sent shock waves of excitement through the scientific world. Hawking was named a fellow of the Royal Society at the age of 32, and later earned the prestigious Albert Einstein Award, among other honors. He also earned teaching stints at Caltech in Pasadena, California, where he served as visiting professor, and at Gonville and Caius College in Cambridge.
In August 2015, Hawking appeared at a conference in Sweden to discuss new theories about black holes and the vexing “information paradox.” Addressing the issue of what becomes of an object that enters a black hole, Hawking proposed that information about the physical state of the object is stored in 2D form within an outer boundary known as the “event horizon.” Noting that black holes “are not the eternal prisons they were once thought,” he left open the possibility that the information could be released into another universe.
Beginning of the Universe
In a March 2018 interview on Neil deGrasse Tyson’s Star Talk, Hawking addressed the topic of “what was around before the Big Bang” by stating there was nothing around. He said by applying a Euclidean approach to quantum gravity, which replaces real time with imaginary time, the history of the universe becomes like a four-dimensional curved surface, with no boundary.
He suggested picturing this reality by thinking of imaginary time and real time as beginning at the Earth’s South Pole, a point of space-time where the normal laws of physics hold; as there is nothing “south” of the South Pole, there was also nothing before the Big Bang.
Hawking and Space Travel
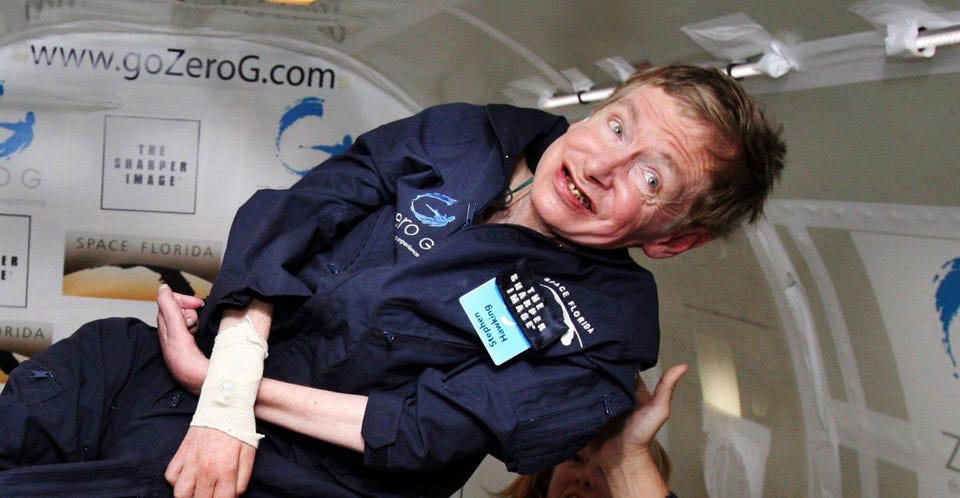
In 2007, at the age of 65, Hawking made an important step toward space travel. While visiting the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, he was given the opportunity to experience an environment without gravity.
Over the course of two hours over the Atlantic, Hawking, a passenger on a modified Boeing 727, was freed from his wheelchair to experience bursts of weightlessness. Pictures of the freely floating physicist splashed across newspapers around the globe.
“The zero-G part was wonderful, and the high-G part was no problem. I could have gone on and on. Space, here I come!” he said.
Hawking was scheduled to fly to the edge of space as one of Sir Richard Branson’s pioneer space tourists. He said in a 2007 statement, “Life on Earth is at the ever-increasing risk of being wiped out by a disaster, such as sudden global warming, nuclear war, a genetically engineered virus or other dangers. I think the human race has no future if it doesn’t go into space. I therefore want to encourage public interest in space.”
Stephen Hawking Movie and TV Appearances
If there is such a thing as a rock-star scientist, Hawking embodied it. His forays into popular culture included guest appearances on The Simpsons, Star Trek: The Next Generation, a comedy spoof with comedian Jim Carrey on Late Night with Conan O’Brien, and even a recorded voice-over on the Pink Floyd song “Keep Talking.”
In 1992, Oscar-winning filmmaker Errol Morris released a documentary about Hawking’s life, aptly titled A Brief History of Time. Other TV and movie appearances included:
‘The Big Bang Theory’
In 2012, Hawking showed off his humorous side on American television, making a guest appearance on The Big Bang Theory. Playing himself on this popular comedy about a group of young, geeky scientists, Hawking brings the theoretical physicist Sheldon Cooper (Jim Parsons) back to Earth after finding an error in his work. Hawking earned kudos for this light-hearted effort.
‘The Theory of Everything’
In November of 2014, a film about the life of Hawking and Jane Wilde was released. The Theory of Everything stars Eddie Redmayne as Hawking and encompasses his early life and school days, his courtship and marriage to Wilde, the progression of his crippling disease and his scientific triumphs.
‘Genius’
In May 2016, Hawking hosted and narrated Genius, a six-part television series which enlists volunteers to tackle scientific questions that have been asked throughout history. In a statement regarding his series, Hawking said Genius is “a project that furthers my lifelong aim to bring science to the public. It’s a fun show that tries to find out if ordinary people are smart enough to think like the greatest minds who ever lived. Being an optimist, I think they will.”
The iBrain
In 2011, Hawkings had participated in a trial of a new headband-styled device called the iBrain. The device is designed to “read” the wearer’s thoughts by picking up “waves of electrical brain signals,” which are then interpreted by a special algorithm, according to an article in The New York Times. This device could be a revolutionary aid to people with ALS.
Hawking on AI
In 2014, Hawking, among other top scientists, spoke out about the possible dangers of artificial intelligence, or AI, calling for more research to be done on all of possible ramifications of AI. Their comments were inspired by the Johnny Depp film Transcendence, which features a clash between humanity and technology.
“Success in creating AI would be the biggest event in human history,” the scientists wrote. “Unfortunately, it might also be the last, unless we learn how to avoid the risks.” The group warned of a time when this technology would be “outsmarting financial markets, out-inventing human researchers, out-manipulating human leaders, and developing weapons we cannot even understand.”
Hawking reiterated this stance while speaking at a technology conference in Lisbon, Portugal, in November 2017. Noting how AI could potentially make gains in wiping out poverty and disease, but could also lead to such theoretically destructive actions as the development of autonomous weapons, he said, “We cannot know if we will be infinitely helped by AI, or ignored by it and sidelined, or conceivably destroyed by it.”
Hawking and Aliens
In July 2015, Hawking held a news conference in London to announce the launch of a project called Breakthrough Listen. Funded by Russian entrepreneur Yuri Milner, Breakthrough Listen was created to devote more resources to the discovery of extraterrestrial life.
Breaking the Internet
In October 2017, Cambridge University posted Hawking’s 1965 doctoral thesis, “Properties of Expanding Universes,” to its website. An overwhelming demand for access promptly crashed the university server, though the document still fielded a staggering 60,000 views before the end of its first day online.
When Did Stephen Hawking Die?
On March 14, 2018, Hawking finally died of ALS, the disease that was supposed to have killed him more than 50 years earlier. A family spokesman confirmed that the iconic scientist died at his home in Cambridge, England.
The news touched many in his field and beyond. Fellow theoretical physicist and author Lawrence Krauss tweeted: “A star just went out in the cosmos. We have lost an amazing human being. Hawking fought and tamed the cosmos bravely for 76 years and taught us all something important about what it truly means to celebrate about being human.”
Hawking’s children followed with a statement: “We are deeply saddened that our beloved father passed away today. He was a great scientist and an extraordinary man whose work and legacy will live on for many years. His courage and persistence with his brilliance and humor inspired people across the world. He once said, ‘It would not be much of a universe if it wasn’t home to the people you love.’ We will miss him forever.”
Later in the month, it was announced that Hawking’s ashes would be interred at Westminster Abbey in London, alongside other scientific luminaries like Isaac Newton and Charles Darwin.
On May 2, 2018, his final paper, titled “A smooth exit from eternal inflation?” was published in the Journal of High Energy Physics. Submitted 10 days before his death, the new report, co-authored by Belgian physicist Thomas Hertog, disputes the idea that the universe will continue to expand.
 Lifeyet News Lifeyet News
Lifeyet News Lifeyet News